Languages in India: Importance of Regional Language in India
The term “regional language” is employed to describe a language spoken by a substantial number of people but is not the primary language of communication for the entire country. A language is categorized as regional when it is predominantly spoken by individuals residing primarily in a specific area within a state or country.
India, often referred to as a “melting pot of cultures,” is equally celebrated for its linguistic diversity. Amidst the multitude of languages spoken across the country, the importance of regional languages stands as a cornerstone in shaping the cultural, social, and educational fabric of the nation.
The Need for Embracing Regional Languages:
It became essential to create an environment where individuals using a regional language in a classroom wouldn’t feel inferior when posing questions or expressing themselves. To alleviate the uncertainty surrounding the favoritism towards the English language.
Numerous studies conducted in India indicated that utilizing a regional language as a medium of instruction can yield positive effects on learning outcomes. It promotes inclusivity and ensures that language is not a barrier hindering effective communication and understanding in educational settings.
The University Grants Commission (UGC) is actively engaging in discussions with diverse regulatory bodies, including the Bar Council of India, to advocate for the promotion of vernacular languages in education. All India Council of Technical Education has taken strides to incorporate regional languages into education. Specifically, courses conducted in regional languages have been introduced in ten colleges.
This progressive approach aims to make education more accessible and inclusive by accommodating the linguistic diversity of the country. It signifies a broader commitment to fostering education that resonates with the cultural and linguistic contexts of the students, paving the way for a more diverse and enriched learning environment.
Importance of Regional Languages in India:
Preserving Cultural Heritage:
Regional languages are repositories of cultural heritage, transmitting traditions, folklore, and historical narratives from generation to generation. Each language carries a unique linguistic fingerprint, offering a window into the rich tapestry of India’s diverse cultural landscape.
Fostering Identity and Belonging:
Language is not merely a means of communication; it is a source of identity. Regional languages connect individuals to their roots, fostering a sense of belonging and pride. They serve as a medium through which communities express their distinctiveness, nurturing a shared cultural consciousness.
Enhancing Communication in Daily Life:
In many parts of India, regional languages are the primary mode of communication in daily life. They play a crucial role in facilitating effective communication within communities, ensuring seamless interaction in various spheres such as family, local businesses, and community events.
Enabling Inclusive Education:
The importance of regional languages in education cannot be overstated. They serve as the initial building blocks of learning, especially in the early years of schooling. Using a child’s mother tongue as the medium of instruction has been shown to enhance comprehension, academic performance, and overall cognitive development.
Promoting Multilingual Proficiency:
India’s multilingual landscape offers a unique advantage — the opportunity for individuals to become proficient in multiple languages. Proficiency in regional languages, in addition to a common language like Hindi or English, not only enriches communication skills but also opens doors to a broader spectrum of cultural understanding.
Preserving Indigenous Knowledge:
Many regional languages are repositories of indigenous knowledge, especially in fields like traditional medicine, agriculture, and handicrafts. Preserving these languages ensures the transmission of valuable knowledge that is often deeply rooted in the local ecosystem.
Facilitating Governance and Administration:
Regional languages play a crucial role in governance and administration at the grassroots level. Local officials and representatives often need to communicate with the public in their native languages to ensure effective and participatory governance.
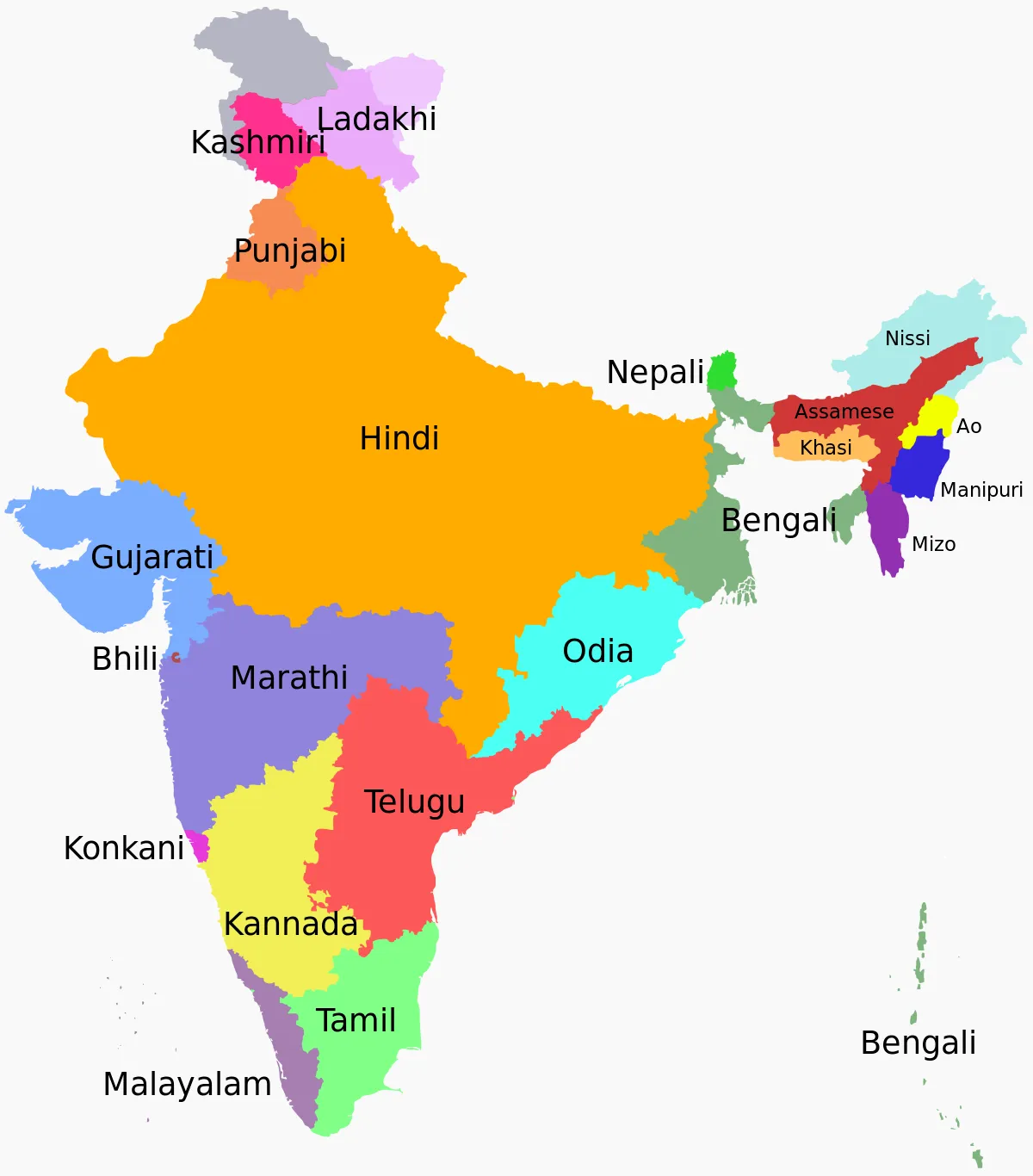
List of Official Languages in India:
| States/UTs: | Official Language: | Second Language: |
| West Bengal: | Bengali and English | Nepali, Urdu, Hindi, Odia, Santali, Rajbanshi, Kurmali, Punajbi, Kamtapuri, Kurukh, and Telugu |
| Uttarakhand: | Hindi | Sanskrit |
| Uttar Pradesh: | Hindi | Urdu |
| Tripura: | Bengali, English, and Kokborok | |
| Telangana: | Telugu | Urdu |
| Tamil Nadu: | Tamil | English |
| Sikkim: | English, Nepali, Sikkimese, and Lepcha | Gurung, Mukhia, Newari, Rai, Limbu, Magar, Sherpa, and Tamang |
| Rajasthan: | Hindi | |
| Punjab: | Punjabi | |
| Odisha: | Odia | |
| Nagaland: | English | |
| Mizoram: | Mizo | English and Hindi |
| Meghalaya: | English | Khasi and Garo |
| Manipur: | Manipuri | English |
| Maharashtra: | Marathi | |
| Madhya Pradesh: | Hindi | |
| Kerala: | Malayalam | English |
| Karnataka: | Kannada | English |
| Jharkhand: | Hindi | Angika, Bengali, Khortha, Kurmali, Kurukh, Bhojpuri, Ho, Kharia, Magahi, Maithili, Mundari, Santali, Nagpuri, Odia, and Urdu |
| Himachal Pradesh: | Hindi | Sanskrit |
| Haryana: | Hindi | English and Punjabi |
| Gujarat: | Gujarati | Hindi |
| Goa: | Konkani and English | Marathi |
| Chhattisgarh: | Hindi | Chhattisgarhi |
| Bihar: | Hindi | Urdu |
| Assam: | Assamese | Bengali and Bodo |
| Arunachal Pradesh: | English | |
| Andhra Pradesh: | Telugu | English |
| Puducherry: | Tamil, French, and English | Telugu and Malayalam |
| Lakshadweep: | Malayalam | English |
| Ladakh: | Hindi and English | |
| Jammu and Kashmir: | Kashmiri, Urdu, Dogri, Hindi, and English | |
| Delhi: | Hindi and English | Urdu and Punjabi |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu: | Gujarati, Konkani, Marathi, and Hindi | |
| Chandigarh: | English | |
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands: | Hindi and English |
Conclusion:
In a country as diverse as India, the importance of regional languages extends far beyond linguistic boundaries. Connecting its people to their roots and each other. Recognizing and celebrating the significance of regional languages is not just a matter of linguistic diversity but an acknowledgment of the vibrant mosaic that is India. As the nation progresses, embracing and preserving these languages becomes not just a cultural imperative but a key to fostering unity in diversity.











 Previous Post
Previous Post